Quantum and Interband Cascade Lasers (QCLs and ICLs), 3 - 11 µm
- Center Wavelengths: 3.00 - 11.00 µm (3333 - 909 cm-1)
- Optical Output Powers Up to 3000 mW
- Broadband Fabry-Perot Lasers and Single-Frequency Distributed Feedback Lasers
QF4600T1
Fabry-Perot Laser,
Ø9 mm TO Can
QD5250C2
Distributed Feedback Laser, Two-Tab C-Mount
QD7500DM1
Distributed Feedback Laser, D-Mount
QD8500HHLH
Distributed Feedback Laser, Horizontal HHL Package
QF4050D3
Fabry-Perot Laser, D-Mount

Please Wait
| Laser Diode Selection Guidea |
|---|
| Shop by Wavelength |
| UV (375 nm) Visible (404 nm - 690 nm) NIR (705 nm - 2000 nm) MIR (3.00 µm - 11.00 µm) |
| Shop by Package / Type |
| Webpage Features | |
|---|---|
| Clicking this icon opens a window that contains specifications and mechanical drawings. | |
| Clicking this icon allows you to download our standard support documentation. | |
|
Choose Item |
Clicking the words "Choose Item" opens a drop-down list containing all of the in-stock lasers around the desired center wavelength. The red icon next to the serial number then allows you to download L-I-V and spectral measurements for that serial-numbered device. |
Features
- Quantum and Interband Cascade Lasers (QCLs and ICLs)
- CW Output Up to 3000 mW
- Center Wavelengths Between 3.00 µm and 11.00 μm (Wavenumbers Between
3333 cm-1 and 909 cm-1) - Broadband Fabry-Perot (FP) and Single-Frequency Distributed Feedback (DFB) Options
- C-Mount, D-Mount, and HHL Lasers are Electrically Isolated from Their Mounts
- Custom Wavelengths, Custom Packages, and OEM Quantities Also Available (Contact Tech Sales for Details)
- Gain Chips with AR-Coated Front Facets Also Available as a Custom Order
Thorlabs' Quantum and Interband Cascade Lasers (QCLs and ICLs) are composed of multiple quantum well heterostructures and utilize intersubband and interband transitions, respectively, to access the mid-infrared spectral region. They are offered in four packages: a two-tab C-mount, a Ø9 mm TO can, a D-mount, and a high heat load (HHL) package with horizontal emission. The two-tab C-mount and Ø9 mm TO can packages can be easily interfaced to our SM1 lens tubes, 30 mm cage systems, and 60 mm cage systems using the LDMC20 C-Mount Laser Mount or the LDM90 Laser Mount, respectively. The D-mount and HHL packages are intended for OEM applications and systems integration. The HHL package can be mounted in Thorlabs' LCM100(/M) Liquid-Cooled Mount for added thermal regulation and protection of the laser diode. Additional information is available in the Packages tab.
Fabry-Perot Lasers
Fabry-Perot quantum and interband cascade lasers exhibit broadband emission in a range spanning roughly 50 cm-1 to 120 cm-1. The laser's specified output power is the sum over the full spectral bandwidth. Since these lasers have broadband emission, they are well suited for medical imaging, illumination, and microscopy applications. The output spectrum and L-I-V curve of each serial-numbered device, measured by an automated test station, are available below and are also included on a data sheet that ships with the device.
Each Fabry-Perot quantum and interband cascade laser has an HR-coated back facet. As a custom option, these lasers can be ordered with an AR coating on the front facet; however, the custom item will operate as a gain chip and not as a CW laser. Although these lasers are specified for CW output, they are compatible with pulsed applications provided that the CW max operating current is not exceeded. For more information or to order a Fabry-Perot QCL or ICL with a tested and specified pulsed optical power or other custom features, please contact Tech Sales.
Distributed Feedback Lasers
Distributed feedback (DFB) quantum and interband cascade lasers emit at a well-defined center wavelength. They provide single longitudinal and single transverse mode operation. By tuning the input current and operating temperature, the output frequency can be tuned over a narrow range between 1 cm-1 and 5 cm-1. They are ideal for chemical sensing (see the Spectroscopy tab), optical communications, and other applications. The output spectrum, power, and L-I-V curve of each serial-numbered device, as measured by an automated test station, are available below and are also included on a data sheet with the laser. These quantum and interband cascade lasers are specified for CW output. While pulsed output is possible, this application prohibits current tuning, and performance is not guaranteed. For two-tab C-Mount and D-Mount lasers, some optical power is emitted through the rear facet; this output is not usable in applications.
Some of Thorlabs' DFB quantum and interband cascade lasers are uniquely suited for gas sensing and analysis. Select high heat load QCLs and ICLs are designed to emit at wavelengths ideal for many gases commonly studied in spectroscopy. These DFB and ICL lasers are guaranteed to reach their specified wavelengths within their tuning range and exhibit single-frequency operation, allowing them to be tuned to specific gas spectra. A list of these QCLs and ICLs with their targeted gas(es) can be found in the Spectroscopy tab, and more information is available by clicking on the info icons (![]() ) next to the relevant Item #s in Tables G1.1 through G13.1.
) next to the relevant Item #s in Tables G1.1 through G13.1.
Mounts, Drivers, and Temperature Control
For two-tab C-mount quantum cascade lasers, we generally recommend the LDMC20 C-Mount Laser Mount and ITC4002QCL or ITC4005QCL Dual Current / Temperature Controller. This device combination includes all the necessary components to mount, drive, and thermally regulate a two-tab C-mount laser. Other compatible current and temperature controllers are listed in the Drivers tab. The LDM90(/M) Laser Mount along with the ITC4002QCL or ITC4005QCL can be used with the TO can lasers, but the 8 W cooling capacity of the LDM90 may limit the driving current of the lasers.
Distributed feedback and Fabry-Perot HHL lasers are compatible with any HHL mount, although cables for HHL packages are typically not rated for the 4.5 A maximum current of the distributed feedback lasers' or the up to 8 A maximum current of the Fabry-Perot lasers' internal thermoelectric coolers. For stable mounting and temperature control of HHL lasers, we recommend using the LCM100(/M) liquid-cooled mount and the CAB4007A or CAB4007B dual LD / TEC connector cables. D-mount lasers require custom mounts. Our ICLs emit a horizontally polarized beam at wavelengths as long as 3.5 µm, while our QCLs emit a vertically polarized beam at wavelengths as long as 11 µm.
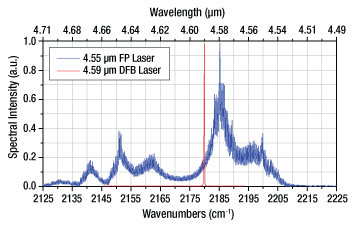
Click to Enlarge
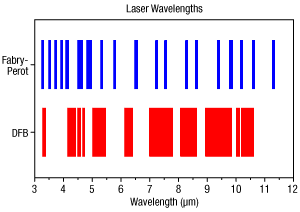
Figure 1.1 Fabry-Perot and Distributed Feedback Laser Comparison:
Fabry-Perot (FP) Lasers have broadband emission, while Distributed Feedback (DFB) Lasers emit at a well defined wavelength.
If designing your own mounting solution, note that due to these lasers' heat loads, the laser must be mounted in a thermally conductive housing to prevent heat buildup. Heat loads for QCLs and ICLs can be up to 70 W, depending upon the wavelength and package. See the Handling tab for additional information.
The typical operating voltages of our QCLs and ICLs can be as high as 16 V and 8 V, respectively. These lasers do not have built-in monitor photodiodes and must be operated in constant current mode.
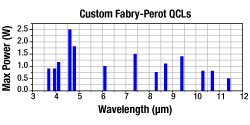
Click to Enlarge
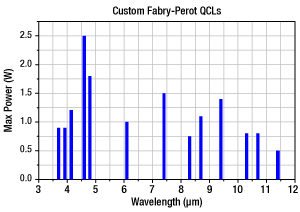
Maximum Output Power of Custom Fabry-Perot QCLs
OEM & Custom QCLs
Thorlabs manufactures custom and OEM quantum cascade lasers in high volumes. We maintain a broad chip inventory at our Jessup, Maryland laser manufacturing facility and we are accustomed to fulfilling specialized requests.
More details are available on the Custom & OEM Lasers tab. To inquire about pricing and availability, please contact us. A semiconductor specialist will contact you within 24 hours or the next business day.
Current and Temperature Controllers
Use Tables 2.1 and 2.2 to select a compatible controller for our MIR lasers. Table 2.1 lists the controllers with which a particular MIR laser is compatible, and Table 2.2 contains selected information on each controller. Complete information on each controller is available in its full web presentation. We particularly recommend our ITC4002QCL and ITC4005QCL controllers, which have high compliance voltages of 17 V and 20 V, respectively. Together, these drivers support the current and voltage requirements of our entire line of Mid-IR Lasers.
The typical operating voltages of our QCLs are 7 - 16 V, while the typical operating voltages of our ICL is 5 V to 8 V. To get L-I-V and spectral measurements of a specific, serial-numbered device, click "Choose Item" next to the part number in the tables below, then click on the Docs Icon next to the serial number of the device.
Laser Mount Compatibility
Thorlabs' LDMC20(/M) C-Mount Laser Mount ships with current and TEC cables for the LDC4005, ITC4001, ITC4002QCL, ITC4005, and ITC4005QCL controllers. To use the LDMC20 with our other controllers, custom cables will be required. For our Ø9 mm TO can QCL we have the LDM90(/M) Laser Mount which is fully compatible with all of the controllers listed in Tables 2.1 and 2.2; however, the mount itself has a limited heat load of 8 W, meaning some QCLs cannot be driven at full power in this mount. If designing your own mounting solution, note that due to these lasers' heat loads, we recommend that they be secured in a thermally conductive housing to prevent heat buildup.
Thorlabs' LCM100(/M) Liquid Cooled Mount is specifically designed to be used with Thorlabs' HHL laser packages. The LCM100(/M) Mount is capable of dissipating heat loads of >140 W at 25 °C, making it an ideal solution for temperature-controlled operation for all of Thorlabs' HHL lasers. For more details on the LCM100(/M) Liquid-Cooled Mount, please see its web presentation here.
The CAB4007B Dual Laser / TEC Connector Cable is designed to be used with any of Thorlabs' HHL laser packages or other HHL lasers with compatible pin settings. The CAB4007B connector cable is rated for up to 10 A of laser and TEC current. The CAB4007A Dual Laser / TEC Connector Cable is designed for use with the LCM100(/M) Mount and is rated for up to 11 A of laser and TEC current. For more details on the CAB4007x cables please see the full web presentation here. Please note that third party cables for these packages are typically not rated for the maximum current of the internal thermoelectric cooler.
If designing your own mounting solution, note that due to these lasers' heat loads, we recommend that they be secured in a thermally conductive housing with sufficient cooling capacity, either active or passive, to prevent heat buildup. Heat loads for DFB QCLs and ICLs can be up to 38 W. The total heat loads for the Fabry-Perot QCL HHL package can be up to 70 W, although a typical heat load from a Fabry-Perot QCL itself is around 20 W.
| Table 2.1 Laser and Controller Compatibility | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Item # | Wavelength | Current Controllers | Dual Current / Temperature Controllers | |
| Small Benchtop | Large Benchtop | Large Benchtop | ||
| ID3250HHLHa | 3.00 to 3.50 µm (3333 to 2857 cm-1) |
LDC205C, LDC210C | LDC4005 | ITC4001, ITC4002QCL |
| ID3271HHLHa | 3.271 µm (3057 cm-1) |
LDC205C, LDC210C | LDC4005 | ITC4001, ITC4002QCL |
| ID3345HHLHa | 3.345 µm (2990 cm-1) |
LDC205C, LDC210C | LDC4005 | ITC4001, ITC4002QCL |
| ID3750HHLHa | 3.50 to 4.00 µm (2857 to 2500 cm-1) |
LDC205C, LDC210C | LDC4005 | ITC4001, ITC4002QCL |
| ID3596HHLHa | 3.596 µm (2781 cm-1) |
LDC205C, LDC210C | LDC4005 | ITC4001, ITC4002QCL |
| QF3850T1 | 3.85 µm (2597 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF3850HHLHb | 3.85 µm (2597 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD4500CM1 | 4.00 to 5.00 µm (2500 to 2000 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD4500HHLHa | 4.00 to 5.00 µm (2500 to 2000 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF4040HHLHb | 4.04 µm (2475 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF4050C2 | 4.05 µm (2469 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF4050D2 | - | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL | |
| QF4050D3 | - | - | ||
| QF4050T2 | - | - | ||
| QF4050T1 | - | - | ||
| QD4235HHa | 4.235 µm (2361 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD4327HHa | 4.327 µm (2311 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD4472HHa | 4.472 µm (2236 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD4540HHa | 4.540 µm (2203 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF4600T2 | 4.60 µm (2174 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF4600T1 | 4.60 µm (2174 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF4600C2 | 4.6 µm (2174 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF4600T3 | 4.60 µm (2174 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF4600D4 | 4.60 µm (2174 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4005QCL |
| QF4600D3 | ||||
| QD4602HHa | 4.602 µm (2173 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF4650HHLHb | 4.65 µm (2151 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD5500CM1 | 5.00 to 6.00 µm (2000 to 1667 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD5500HHLHa | 5.00 to 6.00 µm (2000 to 1667 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD5250C2 | 5.20 to 5.30 µm (1923 to 1887 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD5263HHa | 5.263 µm (1900 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD6500CM1 | 6.00 to 7.00 µm (1667 - 1429 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD6500HHLHa | 6.00 to 7.00 µm (1667 to 1429 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD6134HHa | 6.134 µm (1630 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD7500DM1 | 7.00 to 8.00 µm (1429 to 1250 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD7500HHLHa | 7.00 to 8.00 µm (1429 to 1250 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD7416HHa | 7.416 µm (1348 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD7716HHa | 7.716 µm (1296 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF7900HBc | 7.9 µm (1266 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD7901HHa | 7.901 µm (1266 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD8050CM1 | 8.00 to 8.10 µm (1250 to 1235 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD8500CM1 | 8.00 to 9.00 µm (1250 to 1111 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD8500HHLHa | 8.00 to 9.00 µm (1250 to 1111 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF8450C2 | 8.45 µm (1183 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD8496HHa | 8.496 µm (1177 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF8500HBc | 8.5 µm (1176 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD8912HHa | 8.912 µm (1122.1 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF9150C2 | 9.15 µm (1093 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD9500CM1 | 9.00 to 10.00 µm (1111 to 1000 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD9500HHLHa | 9.00 to 10.00 µm (1111 to 1000 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD9062HHa | 9.062 µm (1103.5 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF9200HBc | 9.2 µm (Typ.) (1087 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD9550C2 | 9.50 to 9.60 µm (1042 to 1053 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QF9500T1 | 9.5 µm (1053 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD9697HHa | 9.697 µm (1031 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD10500CM1 | 10.00 to 11.00 µm (1000 to 909 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD10500HHLHa | 10.00 to 11.00 µm (1000 to 909 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| QD10530HHa | 10.530 µm (949.7 cm -1 ) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL , ITC4005QCL |
| QD10549HHa | 10.549 µm (948 cm -1 ) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL , ITC4005QCL |
| QD10622HHa | 10.622 µm (941 cm-1) |
- | - | ITC4002QCL, ITC4005QCL |
| Table 2.2 Controller Selection Guide | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controller Item # | Controller Type | Controller Package | Current Range | Current Resolution | Voltage | Cables for LDMC20 Laser Mount |
| LDC205C | Current | Small Benchtop (146 x 66 x 290 mm) |
0 to ±0.5 A | 10 µA | >10 V | Not Included with LDMC20a |
| LDC210C | 0 to ±1 A | 100 µA | >10 V | Not Included with LDMC20a | ||
| LDC240C | 0 to ±4 A | 100 µA | >5 V | Not Included with LDMC20a | ||
| LDC4005 | Large Benchtop (263 x 122 x 307 mm) |
0 to 5 A | 1 mA (Front Panel) 80 µA (Remote Control) |
12 V | Included with LDMC20 | |
| LDC8010 | Rack Mounted | 0 to ±1 A | 15 µA | >5 V | Not Included with LDMC20a | |
| LDC8020 | 0 to ±2 A | 30 µA | >5 V | Not Included with LDMC20a | ||
| LDC8040 | 0 to ±4 A | 70 µA | >5 V | Not Included with LDMC20a | ||
| ITC4001 | Current / Temperature | Large Benchtop (263 x 122 x 307 mm) |
0 to 1 A | 100 µA (Front Panel) 16 µA (Remote Control) |
11 V | Included with LDMC20 |
| ITC4002QCL | 0 to 2 A | 100 µA (Front Panel) 32 µA (Remote Control) |
17 V | Included with LDMC20 | ||
| ITC4005 | 0 to 5 A | 1 mA (Front Panel) 80 µA (Remote Control) |
12 V | Included with LDMC20 | ||
| ITC4005QCL | 20 V | Included with LDMC20 | ||||
Packages
Thorlabs stocks quantum cascade lasers (QCLs) in four packages: a two-tab C-mount recommended for academic and industrial research, D-mount and high heat load packages with horizontal emission intended for OEM applications and system integration, and a Ø9 mm TO can for easy integration into standard mounts. Please see the Handling tab for more tips and information for handling these laser packages. Other packages may be available as custom orders (see the Custom & OEM Lasers tab).

Click to Enlarge
Figure 3.1 Two-Tab C-Mount Package
Two-Tab C-Mount
The two-tab C-mount measures 6.4 mm x 4.3 mm x 7.9 mm (not including the tabs), provides high thermal conductivity, and can be secured using a 2-56 or M2 screw with the counterbored Ø2.4 mm (Ø0.09") through hole. The drive voltage and current are supplied through the tabs. As measured from the bottom of the C-mount, the emission height of the QCLs is either 7.15 mm or 7.39 mm depending on the chosen laser; the outer dimensions of the C-mounts are the same. All two-tab C-mount lasers sold on this page are electrically isolated from their C-mounts.

Click for Details
Figure 3.2 Comparison of D-Mount Packages
D-Mount
Designed for OEM customers, our D-mount packages measure 12.0 mm long and have a 2.6 mm emission height. They provide high thermal conductivity and are offered in
4.5 mm, 6.0 mm, or 7.5 mm sizes (measured by cavity length). Note that our DFB D-mount is 2.8 mm thick, whereas our FP D-mounts are 2.1 mm thick. Additionally, our D-mount packages are machined with two counterbored slots for mounting. The drive voltage and current are supplied via two large gold contact pads, which are suitable for wire bonding or probe connections. The lasers are electrically isolated from their D-mounts. A built-in thermistor provides real-time temperature measurements for control electronics.

Click to Enlarge
Figure 3.3 Horizontal HHL Package
High Heat Load Package with Horizontal Emission
This package offers an industry-standard pinout and package dimensions. Each package incorporates a built-in thermistor and thermoelectric cooler (TEC) for active temperature management and prolonged laser lifetime, and also includes an internal aspheric lens that collimates the laser's output. As measured from the bottom of the package, the emission height is 12.7 ± 0.13 mm. The emitted light is coupled out of the package through a wedged zinc sulfide (ZnS) window. The output beam of the Distributed Feedback lasers will deviate downward from the normal by either 2.0° ± 1.5° or 2.0° ± 0.75°, while the output beam of the Fabry-Perot lasers will deviate downward from the normal by 2.0° ± 0.6° or 2.0° ± 0.75°. Each laser is electrically isolated from its mount. More information is available at its Distributed Feedback and Fabry-Perot web presentations.

Click to Enlarge
Figure 3.4 Ø9 mm TO Can Package
Ø9 mm TO Can
The Ø9 mm TO can provides high thermal conductivity, and can be easily integrated into a standard mount for high-power TO can laser diodes. This package incorporates an additional copper disk for added heat dissipation. The additional material makes this TO can thicker than standard; however, the laser is still compatible with all Ø9 mm laser mounts. An AR-coated ZnSe window protects the QCL from dust and debris. The drive voltage and current are supplied through the pins. The emission of the QCL is centered in the TO can.
Do
|
Do Not
|
Handling Two-Tab C-Mount, TO Can, D-Mount, and High Heat Load Lasers
Proper precautions must be taken when handling and using two-tab C-mount, TO Can, D-mount, or high heat load (HHL) lasers. Otherwise, permanent damage to the device will occur. Members of our Technical Support staff are available to discuss possible operation issues.
Avoid Static
Since these lasers are sensitive to electrostatic shock, they should always be handled using standard static avoidance practices.
Avoid Dust and Other Particulates
Unlike TO can and butterfly packages, the laser chip of a C-mount or D-mount laser is exposed to air; hence, there is no protection for the delicate laser chip. Contamination of the laser facets must be avoided. Do not blow on the laser or expose it to smoke, dust, oils, or adhesive films. The laser facet is particularly sensitive to dust accumulation. During standard operation, dust can burn onto this facet, which will lead to premature degradation of the laser. If operating a C-mount or D-mount laser for long periods of time outside a cleanroom, it should be sealed in a container to prevent dust accumulation.
HHL lasers and TO cans are sealed (although the seal is not hermetic), so the laser chip will not be exposed to air. However, similar dust avoidance precautions should be followed for the window on these packages, since the windows are exposed to the atmosphere.
Use a Current Source Specifically Designed for Lasers
These lasers should always be used with a high-quality constant current driver specifically designed for use with lasers, such as any current controller listed in the Drivers tab. Lab-grade power supplies will not provide the low current noise required for stable operation, nor will they prevent current spikes that result in immediate and permanent damage.
Thermally Regulate the Laser
Temperature regulation is required to operate the laser for any amount of time. The temperature regulation apparatus should be rated to dissipate the maximum heat load that can be drawn by the laser. For our two-tab C-mount or TO can quantum cascade lasers, this value can be up to 18 W. The LDMC20(/M) C-Mount Laser Mount, which is compatible with our two-tab C-mount package, is rated for >20 W of heat dissipation. The LDM90(/M) Ø9 mm TO Can Laser Mount is only rated for 8 W of heat dissipation, so it cannot operate some quantum cascade lasers at full power. Our DFB D-mount laser's maximum heat load is 7.2 W, our FP D-mount lasers' maximum heat load is 35 W, our HHL FP QCLs have a max heat load of 70 W, and our HHL DFB QCLs and ICL have a maximum heat load of 38 W. The LCM100(/M) Liquid-Cooled Mount is compatible with all standard HHL packages and is capable of dissipating up to 140 W of heat at 25 °C.
The back face of the C-mount package and the bottom face of the D-mount or high heat load package is machined flat to make proper thermal contact with a heat sink. Ideally, the heat sink will be actively regulated to ensure proper heat conduction. A Thermoelectric Cooler (TEC) is well suited for this task and can easily be incorporated into any standard PID controller. The HHL package incorporates a suitable TEC.
A fan may serve to move the heat away from the TEC and prevent thermal runaway. However, the fan should not blow air on or at the laser itself. Water cooling methods may also be employed for temperature regulation. Although thermal grease is acceptable for TO can and HHL lasers, it should not be used with two-tab C-mount or D-mount lasers, since it can creep, eventually contaminating the laser facet. Pyrolytic graphite is an acceptable alternative to thermal grease for these cases. Solder can also be used to thermally regulate two-tab C-mount lasers, although controlling the thermal resistance at the interface is important for best results. Solder is not recommended for thermal regulation of D-mount or HHL lasers.
For assistance in picking a suitable temperature controller for your application please contact Tech Support.
Carefully Make Electrical Connections
When making electrical connections, care must be taken. The flux fumes created by soldering can cause laser damage, so care must be taken to avoid this.
Solder can be avoided entirely for two-tab C-mount and TO can lasers by using the LDMC20 or LDM90 laser mounts, respectively. If soldering to the tabs on a two-tab C-mount, solder with the C-mount already attached to a heat sink to avoid unnecessary heating of the laser chip. We do not recommend soldering lasers in TO can packages.
Although soldering to the leads of our HHL lasers is possible, we generally recommend using cables specifically designed for HHL packages. Thorlabs' CAB4007B LD / TEC cable is specifically designed to connect any standard 10-pin HHL laser package directly to the ITC400xQCL series of laser diode and TEC controllers. The CAB4007A LD / TEC cable can be used to connect an ITC400xQCL controller directly to the LCM100(/M) mount. Please note that third-party cables for high heat load packages are typically not rated for the 4.5 A maximum current of the distributed feedback lasers' or the up to 8 A maximum current of the Fabry-Perot lasers' internal thermoelectric coolers. If soldering to the leads on an HHL package, the maximum soldering temperature and time are 250 °C and 10 seconds, respectively.
For D-mount lasers, solder should never be used; wire bonding or probe connections are the only recommended methods.
Minimize Physical Handling
As any interaction with the package carries the risk of contamination and damage, any movement of the laser should be planned in advance and carefully carried out. It is important to avoid mechanical shocks. Dropping the laser package from any height can cause the unit to permanently fail.
Choosing a Collimating Lens
Since the output of our MIR lasers is highly divergent, collimating optics are necessary. Aspheric lenses, which are corrected for spherical aberration, are commonly chosen when the desired beam diameter is between 1 - 5 mm. The simple example below illustrates the key specifications to consider when choosing the correct lens for a given application. Please note that lasers in a high heat load (HHL) package are already collimated using a lens integrated into the package.
The following example uses our previous generation 3.8 µm Interband Cascade Laser.
Key Specifications
- Center Wavelength: 3.80 µm
- Parallel Beam Divergence Angle: 40°
- Perpendicular Beam Divergence Angle: 60°
- Desired Collimated Beam Diameter: 4 mm (Major Axis)
The specifications for the laser indicate that the typical parallel and perpendicular FWHM divergences are 40° and 60°, respectively. Therefore, as the light propagates, an elliptical beam will result. To collect as much light as possible during the collimation process, consider the larger of these two divergence angles in your calculations (in this case, 60°).
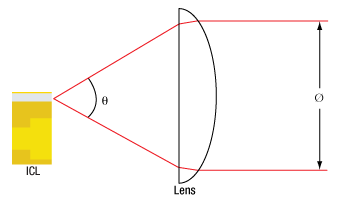
θ = Divergence Angle
Ø = Beam Diameter
Using the information above, the focal length needed to obtain the desired beam diameter can be calculated:
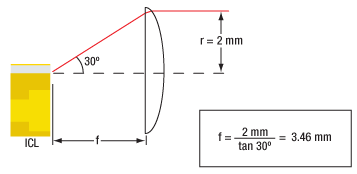
This information allows the appropriate collimating lens to be selected. Thorlabs offers a large selection of black diamond aspheric lenses for the mid-IR spectral range. Since this laser emits at 3.80 µm, the best AR coating is our -E coating, which provides Ravg < 0.6% per surface from 3 to 5 µm. The lenses with focal lengths closest to the calculated value of 3.46 mm are our 390036-E (unmounted) or C036TME-E (mounted) Molded Aspheric Lenses, which have f = 4.00 mm. Plugging this focal length back into the equation shown above gives a final beam diameter of 4.62 mm along the major axis.
Next, we verify that the numerical aperture (NA) of the lens is larger than the NA of the laser:
NALens = 0.56
NALaser ~ sin (30°) = 0.5
NALens > NALaser
Since NALens > NALaser, the 390036-E or C036TME-E lenses will give acceptable beam quality. However, by using the FWHM beam diameter, we have not accounted for a significant fraction of the beam power. A better practice is to use the 1/e2 beam diameter. For a Gaussian beam profile, the 1/e2 beam diameter is approximately equal to 1.7X the FWHM diameter. The 1/e2 beam diameter is therefore a more conservative estimate of the beam size, containing more of the laser's intensity. Using this value significantly reduces far-field diffraction (since less of the incident light is clipped) and increases the power delivered after the lens.
A good rule of thumb is to pick a lens with an NA of twice the NA of the laser diode. For example, either the 390037-E or the C037TME-E could be used as these lenses each have an NA of 0.85, which a little less than twice that of our IF3800CM2 laser (NA 0.5). Compared to the first set of lenses we identified, these have a shorter focal length of 1.873 mm, resulting in a smaller final beam diameter of 2.16 mm.
Beam Profile Characterization of a Mid-IR Laser
Because quantum cascade lasers (QCLs) and interband cascade lasers (ICLs) have intrinsically large divergence angles, it is necessary to install collimating optics in front of the laser facet. We are frequently asked what beam quality can be reasonably expected once the beam has been collimated. This tab presents an M2 measurement we performed using a collimated QCL laser in a High Heat Load (HHL) package.
For this system, we obtained M2 = 1.04 ± 0.01 in the parallel direction and M2 = 1.00 ± 0.02 in the perpendicular direction. We perform an M2 measurement on all collimated QCLs and ICLs in HHL packages to ensure that the beam quality specification is met (M2 < 1.3). Similar results would be obtained when collimating any Thorlabs QCL or ICL device (TO can, two-tab C-mount, or D-mount) with the appropriate aspheric lens.
Experimental Setup
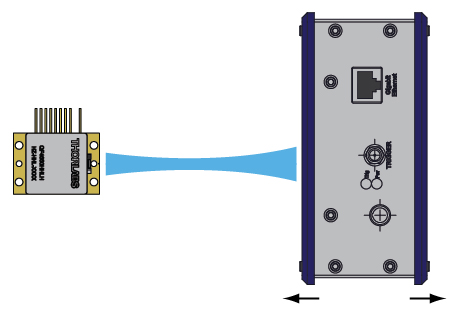
Click to Enlarge
Figure 817A This schematic shows the setup for beam profile measurements of a QF4650HHLH quantum cascade laser. A pyroelectric camera was translated along the beam propagation direction to obtain beam profiles at various distances from the QCL.
The apparatus we used to determine M2 is shown schematically in Figure 817A. To ensure that our results were rigorous, all data acquisition and analysis were consistent with the ISO 11146 standard.
The QF4650HHLH Quantum Cascade Laser used for this measurement emitted CW laser light with a center wavelength of 4.595 µm. The laser was temperature stabilized at 25 °C using the HHL’s internal thermistor and TEC. The output beam was collimated by a 390037-E lens placed immediately in front of the laser facet within the HHL. This lens was selected because of its large NA of 0.85 (which helped maximize collection of the emitted light) and because of its AR coating (Ravg < 0.6% per surface from 3 µm to 5 µm). The laser had an output power of about 20 mW during this measurement.
A pyroelectric camera (Spiricon Pyrocam III-HR) with 80 µm square pixels was scanned along the beam propagation direction, and the beam width was measured along the parallel and perpendicular directions. The beam profiler has several different methods for determining the beam width from the measured beam profile. We found that the best results were obtained by using the 90-10 knife-edge method, where an algorithm is used to simulate scanning a knife-edge across the beam and finding the points of 10% and 90% power. These widths are then converted to the equivalent widths using the second-order moment (D4σ) definition so that they can be used in determining M2 while following the ISO standard. Hyperbolas were fit to the beam width to extract M2 for each beam axis. The camera's internal chopper was triggered at 50 Hz since the pyroelectric effect is sensitive to changes in temperature rather than absolute temperature differences.
Data Analysis
Figure 817B shows the second-order moment (D4σ) beam widths for the parallel and perpendicular directions as a function of distance from the laser. Along the parallel direction, we obtained a minimum beam width of 1.5 mm, while along the perpendicular direction, we obtained a minimum beam width of 1.4 mm. The spatial profiles were observed along the beam path using the pyroelectric camera, with two examples shown in Figures 817D and 817E.
The divergence of the beam can be described by a hyperbola, as written in Equation 1:
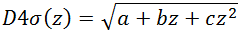 |
(Eq. 1) |
In order to obtain the hyperbola coefficients a, b, and c for the parallel and perpendicular directions, we fit the discrete beam width measurements along each direction to hyperbolas, as shown in the graph in Figure 817B These coefficients were substituted into Equation 2 (taking λ = 4.595 µm) to yield M2.
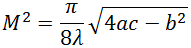 |
(Eq. 2) |
The hyperbola coefficients and M2 values derived by this method are listed in Table 817C.
| Table 817C Hyperbola Coefficients and M2 Values | ||
|---|---|---|
| Value | Parallel | Perpendicular |
| a | 3.82 ± 0.03 mm2 | 5.71 ± 0.04 mm2 |
| b | -0.0110 ± 0.0001 mm | -0.0169 ± 0.0001 mm |
| c | (1.764 ± 0.008) × 10-5 | (1.856 ± 0.009) × 10-5 |
| M2 | 1.04 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.2 |
As shown by the graph in Figure 817B, the beam waist of the parallel direction occurred around z = 300 mm, while the beam waist of the perpendicular direction occurred around z = 450 mm. The small astigmatism corresponds closely to what is expected for this laser given the emitter shape and beam divergences.
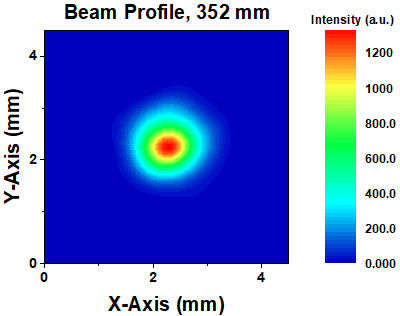
Click to Enlarge
Figure 817D Beam Profile near Beam Waists, 352 mm from Laser
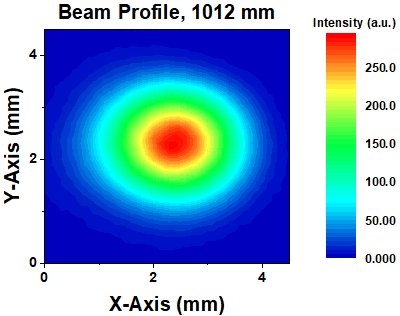
Click to Enlarge
Figure 817E Beam Profile after Propagation, 1012 mm from Laser
| Selected Distributed Feedback QCLs and ICLsa | ||
|---|---|---|
| Item # | Nominal Center Frequency | Targeted Gas(es) |
| ID3250HHLH | 3076 cm-1 (3.25 µm) | CH4 (Methane) |
| ID3271HH | 3057 cm-1 (3.271 µm) | CH4 (Methane) |
| ID3345HH | 2990 cm-1 (3.345 µm) | CH4 (Methane) C2H6 (Ethane) |
| ID3750HHLH | 2667 cm-1 (3.75 µm) | H2CO (Formaldehyde) |
| ID3596HH | 2781 cm-1 (3.596 µm) | H2CO (Formaldehyde) |
| QD4235HH | 2361 cm -1 (4.235 µm) | CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) |
| QD4327HH | 2311 cm -1 (4.327 µm) | CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) |
| QD4472HH | 2236 cm-1 (4.472 µm) | N2O (Nitrous Oxide) |
| QD4540HH | 2203 cm-1 (4.540 µm) | N2O (Nitrous Oxide) |
| QD4602HH | 2173 cm-1 (4.602 µm) | CO (Carbon Monoxide) |
| QD5250C2 | 1905 cm-1 (5.25 µm) | NO (Nitric Oxide) |
| QD5263HH | 1900 cm-1 (5.263 µm) | NO (Nitric Oxide) |
| QD6134HH | 1630 cm-1 (6.134 µm) | NO2 (Nitrogen Dioxide) |
| QD7416HH | 1348 cm-1 (7.416 µm) | SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) |
| QD7716HH | 1296 cm-1 (7.716 µm) | N2O (Nitrous Oxide) |
| QD7901HH | 1266 cm-1 (7.901 µm) | H2S (Hydrogen Sulfide) |
| QD8050CM1 | 1242 cm-1 (8.05 µm) | CH4 (Methane) HONO (Nitrous Acid) |
| QD8496HH | 1177 cm-1 (8.496 µm) | 12CH3D (Methane Isotopologue) |
| QD8912HH | 1122.1 cm-1 (8.912 µm) | NH3 (Ammonia) |
| QD9062HH | 1103.5 cm-1 (9.062 µm) | NH3 (Ammonia) |
| QD9550C2 | 1047 cm-1 (9.55 µm) | NH3 (Ammonia) |
| QD9697HH | 1031 cm-1 (9.697 µm) | O3 (Ozone) |
| QD10530HH | 949.7 cm-1 (10.530 µm) | C2H4 (Ethylene) |
| QD10549HH | 948 cm-1 (10.549 µm) | SF6 (Sulfur Hexafluoride) |
| QD10622HH | 941 cm-1 (10.622 µm) | N2H4 (Hydrazine) |
Gas-Phase Spectroscopy Using Distributed Feedback Lasers
Distributed Feedback Quantum and Interband Cascade Lasers (DFB QCLs and ICLs) offer many attractive features for spectroscopy. They emit at a single wavelength within the mid-IR, where many gaseous species characteristically absorb. Moreover, their emission wavelength is easily tuned (typical tuning range: 1 - 5 cm-1) by changing the drive current and operating temperature of the laser, making them ideal for isolating narrow gas absorption lines. Finally, quantum cascade lasers offer relatively high output power (typically 40 - 120 mW at rollover current), helping improve measurement sensitivity. ICLs will typically have a low output power, but a far lower power consumption.
Thorlabs' DFB QCLs emit at wavelengths that range from 4.00 to 11.00 µm (2500 cm-1 to 909 cm-1), while our DFB ICLs emit at wavelengths that range from 3.00 to 4.00 µm (3333 cm-1 to 2500 cm-1). If we do not stock the wavelength required for your application, custom wavelengths are available by contacting Tech Sales.
The tuning range of individual DFB QCLs and ICLs depends greatly on the actual laser device. Each DFB QCL or ICL is a unique device with its own threshold current, rollover current, and spectrum. Since the wavelength and power of DFB QCLs and ICLs change over the tuning range, operating the lasers near the rollover current is not always desirable in spectroscopy measurements, which require specific wavelengths. The driving current and operating temperature of DFB QCLs and ICLs can be adjusted to change the output signal to the desired wavelength and power.
DFB QCLs and ICLs are ideal for use in photoacoustic spectroscopy, a technique based on the photoacoustic effect that is able to accurately detect trace gas concentrations for a wide variety of applications. Thorlabs offers an Acoustic Detection Module that can be used with our DFB QCLs and ICLs to build custom QEPAS sensors that target the absorption of a specific gas. We also offer a Quartz-Enhanced Photoacoustic Sensor that targets a methane absorption line to detect trace amounts of methane in a gas.
Tuning Example
To demonstrate the tunability of these lasers, we measured the center wavelength of a previous-generation QD4580CM1 DFB QCL as a function of drive current, from threshold to near rollover, at 15 °C and 25 °C. Over the entire temperature and drive current range, we obtained center wavelengths from 4.568 µm to 4.586 µm (2189.14 cm-1 to 2180.77 cm-1), spanning a range of 18 nm (8.37 cm-1), with output power ranging from 3.2 mW (at threshold current) to 39.1 mW (at near-rollover current). Since the laser is capable of operating at 35 °C, even broader wavelength tuning is also achievable.
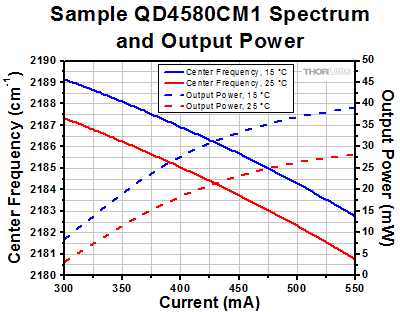
Click to Enlarge
Figure 7.1 DFB QCL Center Frequency as Function of Temperature and Drive Current
| Sample QD4580CM1a Spectrum and Output Power | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current | 15 °C | 25 °C | ||
| Center Frequency | Output Power |
Center Frequency | Output Power |
|
| 300 mA | 2189.14 cm-1 (4.568 µm) | 8.4 mW | 2187.34 cm-1 (4.572 µm) | 3.2 mW |
| 350 mA | 2188.12 cm-1 (4.570 µm) | 19.6 mW | 2186.26 cm-1 (4.574 µm) | 11.9 mW |
| 400 mA | 2186.92 cm-1 (4.573 µm) | 28.3 mW | 2185.05 cm-1 (4.577 µm) | 18.9 mW |
| 450 mA | 2185.71 cm-1 (4.575 µm) | 33.7 mW | 2183.78 cm-1 (4.579 µm) | 23.5 mW |
| 500 mA | 2184.33 cm-1 (4.578 µm) | 37.1 mW | 2182.34 cm-1 (4.582 µm) | 26.6 mW |
| 550 mA | 2182.76 cm-1 (4.581 µm) | 39.1 mW | 2180.77 cm-1 (4.586 µm) | 28.2 mW |
Click to Enlarge
Figure 166B Some of Our Available Packages

Click for Details
Figure 166A Wire Bonding a Quantum Cascade Laser on a C-Mount
Custom & OEM Quantum Cascade and Interband Cascade Lasers
At our semiconductor manufacturing facility in Jessup, Maryland, we build fully packaged mid-IR lasers and gain chips. Our engineering team performs in-house epitaxial growth, wafer fabrication, and laser packaging. We maintain chip inventory from 3 µm to 12 µm, and our vertically integrated facilities are well equipped to fulfill unique requests.
High-Power Fabry-Perot QCLs
For Fabry-Perot lasers, we can reach multi-watt output power on certain custom orders. The available power depends upon several factors, including the wavelength and the desired package.
DFB QCLs at Custom Wavelengths
For distributed feedback (DFB) lasers, we can deliver a wide range of center wavelengths with user-defined wavelength precision. Our semiconductor specialists will take your application requirements into account when discussing the options with you.
Figures 166A through 166E illustrate some of our custom capabilities. Please visit our semiconductor manufacturing capabilities presentation to learn more.
Click to Enlarge
Figure 166C Available Wavelengths for Custom QCLs and ICLs
Click to Enlarge
Figure 166D Maximum Output Power of Custom Fabry-Perot QCLs
Click to Enlarge
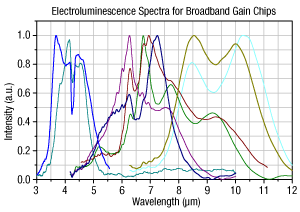
Figure 166E Electroluminescence Spectra of Available Gain Chip Material
Insights into QCLs and ICLs
Scroll down to read about:
- Labels Used to Identify Perpendicular and Parallel Components
- QCLs and ICLs: Operating Limits and Thermal Rollover
Click here for more insights into lab practices and equipment.
Labels Used to Identify Perpendicular and Parallel Components
When polarized light is incident on a surface, it is often described in terms of perpendicular and parallel components. These are orthogonal to each other and the direction in which the light is propagating (Video 184A).
Labels and symbols applied to the perpendicular and parallel components can make it difficult to determine which is which. Table 184B identifies, for a variety of different sets, which label refers to the perpendicular component and which to the parallel.
| Table 184B Common Labels for Orthogonal Linear Polarization States | ||
|---|---|---|
| Labels | Notes |
|
| Perpendicular | Parallel | |
| s | p | Senkrecht (s) is 'perpendicular' in German. Parallel begins with 'p.' |
| TE | TM | TE: Transverse electric field. |
| ⊥ | // | ⊥ and // are symbols for perpendicular and parallel, respectively. |
| σ | π | The Greek letters corresponding to s and p are σ and π, respectively. |
| Sagittal | Tangential | A sagittal plane is a longitudinal plane that divides a body. |
The perpendicular and parallel directions are referenced to the plane of incidence, which is illustrated in Video 184A for a beam reflecting from a surface. Together, the incident ray and the surface normal define the plane of incidence, and the incident and reflected rays are both contained in this plane. The perpendicular direction is normal to the plane of incidence, and the parallel direction is in the plane of incidence.
The electric fields of the perpendicular and parallel components oscillate in planes that are orthogonal to one another. The electric field of the perpendicular component oscillates in a plane perpendicular to the plane of incidence, while the electric field of the parallel component oscillated in the plane of incidence. The polarization of the light beam is the vector sum of the perpendicular and parallel components.
Normally Incident Light
Since a plane of incidence cannot be defined for normally incident light, this approach cannot be used to unambiguously define perpendicular and parallel components of light. There is limited need to make the distinction, since under conditions of normal incidence the reflectivity is the same for all components of light.
Date of Last Edit: Mar. 5, 2020
QCLs and ICLs: Operating Limits and Thermal Rollover
Click to Enlarge
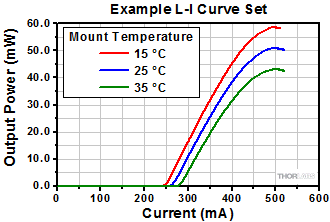
Figure 184D This set of L-I curves for a QCL laser illustrates that the mount temperature can affect the peak operating temperature, but that using a temperature controlled mount does not remove the danger of applying a driving current large enough to exceed the rollover point and risk damaging the laser.
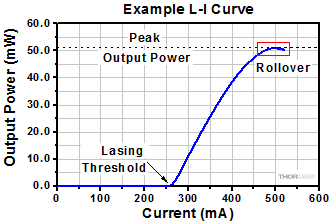
Click to Enlarge
Figure 184C This example of an L-I curve for a QCL laser illustrates the typical non-linear slope and rollover region exhibited by QCL and ICL lasers. Operating parameters determine the heat load carried by the lasing region, which influences the peak output power. This laser was installed in a temperature controlled mount set to 25 °C.
The light vs. driving current (L-I) curves measured for quantum and interband cascade Lasers (QCLs and ICLs) include a rollover region, which is enclosed by the red box in Figure 184C.
The rollover region includes the peak output power of the laser, which corresponds to a driving current of just under 500 mA in this example. Applying higher drive currents risks damaging the laser.
Laser Operation
These lasers operate by forcing electrons down a controlled series of energy steps, which are created by the laser's semiconductor layer structure and an applied bias voltage. The driving current supplies the electrons.
An electron must give up some of its energy to drop down to a lower energy level. When an electron descends one of the laser's energy steps, the electron loses energy in the form of a photon. But, the electron can also lose energy by giving it to the semiconductor material as heat, instead of emitting a photon.
Heat Build Up
Lasers are not 100% efficient in forcing electrons to surrender their energy in the form of photons. The electrons that lose their energy as heat cause the temperature of the lasing region to increase.
Conversely, heat in the lasing region can be absorbed by electrons. This boost in energy can scatter electrons away from the path leading down the laser's energy steps. Later, scattered electrons typically lose energy as heat, instead of as photons.
As the temperature of the lasing region increases, more electrons are scattered, and a smaller fraction of them produce light instead of heat. Rising temperatures can also result in changes to the laser's energy levels that make it harder for electrons to emit photons. These processes work together to increase the temperature of the lasing region and to decrease the efficiency with which the laser converts current to laser light.
Operating Limits are Determined by the Heat Load
Ideally, the slope of the L-I curve would be linear above the threshold current, which is around 270 mA in Figure 184C. Instead, the slope decreases as the driving current increases, which is due to the effects from the rising temperature of the lasing region. Rollover occurs when the laser is no longer effective in converting additional current to laser light. Instead, the extra driving creates only heat. When the current is high enough, the strong localized heating of the laser region will cause the laser to fail.
A temperature controlled mount is typically necessary to help manage the temperature of the lasing region. But, since the thermal conductivity of the semiconductor material is not high, heat can still build up in the lasing region. As illustrated in Figure 184D, the mount temperature affects the peak optical output power but does not prevent rollover.
The maximum drive current and the maximum optical output power of QCLs and ICLs depend on the operating conditions, since these determine the heat load of the lasing region.
Date of Last Edit: Dec. 4, 2019
| Posted Comments: | |
user
(posted 2022-02-16 10:22:33.18) The tabulated data for the QF4650HHLH indicates that it has an output power of 1500 W. Likely a typo, should be 1500 mW. cdolbashian
(posted 2022-02-16 11:22:53.0) Thank you for finding this error on our website! The value should indeed be 1500mW. We will be correcting it in the near future. Jean-Michel Melkonian
(posted 2021-07-01 09:11:20.76) Dear thorlabs,
do you offer solutions (or are planning to) to modulate the QCL current at frequencies above 100 kHz ? 1MHz for instance.
This should require special electronics, and careful impedance matching, something that your standard controllers cannot do.
This has applications in free space communications
thanks YLohia
(posted 2021-07-01 10:30:11.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Unfortunately, we currently do not have any plans of offering such solutions. That being said, we will consider something like this in the future. user
(posted 2016-10-14 11:21:05.987) We need the MIR light visualize to check collimation. Which part number should we choose. Let us know the web link? jlow
(posted 2016-10-14 12:08:44.0) Response from Jeremy at Thorlabs: You can use the VRC6 to help visualize the MIR light. |
| The rows shaded green below denote single-frequency lasers. |
| Item # | Wavelength | Output Power | Operating Current | Operating Voltage | Beam Divergence | Laser Mode | Package | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel | Perpendicular | |||||||
| L375P70MLD | 375 nm | 70 mW | 110 mA | 5.4 V | 9° | 22.5° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L404P400M | 404 nm | 400 mW | 370 mA | 4.9 V | 13° (1/e2) | 42° (1/e2) | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP405-SF10 | 405 nm | 10 mW | 50 mA | 5.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L405P20 | 405 nm | 20 mW | 38 mA | 4.8 V | 8.5° | 19° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP405C1 | 405 nm | 30 mW | 75 mA | 4.3 V | 1.4 mrad | 1.4 mrad | Single Transverse Mode | Ø3.8 mm, SM Pigtail with Collimator |
| L405G2 | 405 nm | 35 mW | 50 mA | 4.9 V | 10° | 21° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø3.8 mm |
| DL5146-101S | 405 nm | 40 mW | 70 mA | 5.2 V | 8° | 19° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L405A1 | 405 nm | 175 mW (Min) | 150 mA | 5.0 V | 9° | 20° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP405-MF300 | 405 nm | 300 mW | 350 mA | 4.5 V | - | - | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm, MM Pigtail |
| L405G1 | 405 nm | 1000 mW | 900 mA | 5.0 V | 13° | 45° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| LP450-SF25 | 450 nm | 25 mW | 75 mA | 5.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L450G3 | 450 nm | 100 mW (Min) | 80 mA | 5.2 V | 8.4° | 21.5° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø3.8 mm |
| L450G2 | 450 nm | 100 mW (Min) | 80 mA | 5.0 V | 8.4° | 21.5° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L450P1600MM | 450 nm | 1600 mW | 1200 mA | 4.8 V | 7° | 19 - 27° | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L473P100 | 473 nm | 100 mW | 120 mA | 5.7 V | 10 | 24 | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP488-SF20 | 488 nm | 20 mW | 70 mA | 6.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP488-SF20G | 488 nm | 20 mW | 80 mA | 5.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L488P60 | 488 nm | 60 mW | 75 mA | 6.8 V | 7° | 23° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP505-SA15 | 505 nm | 15 mW | 80 mA | 7.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP505-SF15 | 505 nm | 15 mW | 80 mA | 7.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L505P30 | 505 nm | 30 mW | 80 mA | 6.7 V | 8° | 23° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP514-SA25 | 514 nm | 25 mW | 140 mA | 5.9 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP514-SF25 | 514 nm | 25 mW | 140 mA | 5.9 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L514A2 | 514 nm | 45 mW (Min) | 115 mA | 5.7 V | 8° | 22° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP515-SF3 | 515 nm | 3 mW | 50 mA | 5.3 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L515A1 | 515 nm | 10 mW | 50 mA | 5.4 V | 6.5° | 21° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP520-SF15A | 520 nm | 15 mW | 100 mA | 7.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L520A1 | 520 nm | 30 mW (Min) | 80 mA | 5.5 V | 8° | 22° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP520-SF40 | 520 nm | 40 mW | 190 mA | 6.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| PL520 | 520 nm | 50 mW | 250 mA | 7.0 V | 7° | 22° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø3.8 mm |
| L520P50 | 520 nm | 45 mW | 150 mA | 7.0 V | 7° | 22° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L520A2 | 520 nm | 110 mW (Min) | 225 mA | 5.9 V | 8° | 22° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| DJ532-10 | 532 nm | 10 mW | 220 mA | 1.9 V | 0.69° | 0.69° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9.5 mm (non-standard) |
| DJ532-40 | 532 nm | 40 mW | 330 mA | 1.9 V | 0.69° | 0.69° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9.5 mm (non-standard) |
| LP633-SF50 | 633 nm | 50 mW | 170 mA | 2.6 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL63163DG | 633 nm | 100 mW | 170 mA | 2.6 V | 8.5° | 18° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LPS-635-FC | 635 nm | 2.5 mW | 70 mA | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LPS-PM635-FC | 635 nm | 2.5 mW | 60 mA | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, PM Pigtail |
| L635P5 | 635 nm | 5 mW | 30 mA | <2.7 V | 8° | 32° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL6312G | 635 nm | 5 mW | 50 mA | <2.7 V | 8° | 31° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| LPM-635-SMA | 635 nm | 8 mW | 50 mA | 2.2 V | - | - | Multimode | Ø9 mm, MM Pigtail |
| LP635-SF8 | 635 nm | 8 mW | 60 mA | 2.3 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL6320G | 635 nm | 10 mW | 60 mA | 2.2 V | 8° | 31° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| HL6322G | 635 nm | 15 mW | 75 mA | 2.4 V | 8° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| L637P5 | 637 nm | 5 mW | 20 mA | <2.4 V | 8° | 34° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP637-SF50 | 637 nm | 50 mW | 140 mA | 2.6 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP637-SF70 | 637 nm | 70 mW | 220 mA | 2.7 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL63142DG | 637 nm | 100 mW | 140 mA | 2.7 V | 8° | 18° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL63133DG | 637 nm | 170 mW | 250 mA | 2.8 V | 9° | 17° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL6388MG | 637 nm | 250 mW | 340 mA | 2.3 V | 10° | 40° | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L637G1 | 637 nm | 1200 mW | 1100 mA | 2.5 V | 10° | 32° | Multimode | Ø9 mm (non-standard) |
| L638P040 | 638 nm | 40 mW | 92 mA | 2.4 V | 10° | 21° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L638P150 | 638 nm | 150 mW | 230 mA | 2.7 V | 9 | 18 | Single Transverse Mode | Ø3.8 mm |
| L638P200 | 638 nm | 200 mW | 280 mA | 2.9 V | 8 | 14 | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L638P700M | 638 nm | 700 mW | 820 mA | 2.2 V | 9° | 35° | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL6358MG | 639 nm | 10 mW | 40 mA | 2.4 V | 8° | 21° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL6323MG | 639 nm | 30 mW | 100 mA | 2.5 V | 8.5° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL6362MG | 640 nm | 40 mW | 90 mA | 2.5 V | 10° | 21° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP642-SF20 | 642 nm | 20 mW | 90 mA | 2.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP642-PF20 | 642 nm | 20 mW | 110 mA | 2.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, PM Pigtail |
| HL6364DG | 642 nm | 60 mW | 120 mA | 2.5 V | 10° | 21° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL6366DG | 642 nm | 80 mW | 150 mA | 2.5 V | 10° | 21° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL6385DG | 642 nm | 150 mW | 250 mA | 2.6 V | 9° | 17° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L650P007 | 650 nm | 7 mW | 28 mA | 2.2 V | 9° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LPS-660-FC | 658 nm | 7.5 mW | 65 mA | 2.6 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP660-SF20 | 658 nm | 20 mW | 80 mA | 2.6 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LPM-660-SMA | 658 nm | 22.5 mW | 65 mA | 2.6 V | - | - | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm, MM Pigtail |
| HL6501MG | 658 nm | 30 mW | 75 mA | 2.6 V | 8.5° | 22° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L658P040 | 658 nm | 40 mW | 75 mA | 2.2 V | 10° | 20° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP660-SF40 | 658 nm | 40 mW | 135 mA | 2.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP660-SF60 | 658 nm | 60 mW | 210 mA | 2.4 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL6544FM | 660 nm | 50 mW | 115 mA | 2.3 V | 10° | 17° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP660-SF50 | 660 nm | 50 mW | 140 mA | 2.3 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL6545MG | 660 nm | 120 mW | 170 mA | 2.45 V | 10° | 17° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L660P120 | 660 nm | 120 mW | 175 mA | 2.5 V | 10° | 17° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L670VH1 | 670 nm | 1 mW | 2.5 mA | 2.6 V | 10° | 10° | Single Transverse Mode | TO-46 |
| LPS-675-FC | 670 nm | 2.5 mW | 55 mA | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL6748MG | 670 nm | 10 mW | 30 mA | 2.2 V | 8° | 25° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL6714G | 670 nm | 10 mW | 55 mA | <2.7 V | 8° | 22° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| HL6756MG | 670 nm | 15 mW | 35 mA | 2.3 V | 8° | 24° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP685-SF15 | 685 nm | 15 mW | 55 mA | 2.1 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL6750MG | 685 nm | 50 mW | 70 mA | 2.3 V | 9° | 21° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| HL6738MG | 690 nm | 30 mW | 85 mA | 2.5 V | 8.5° | 19° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP705-SF15 | 705 nm | 15 mW | 55 mA | 2.3 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL7001MG | 705 nm | 40 mW | 75 mA | 2.5 V | 9° | 18° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP730-SF15 | 730 nm | 15 mW | 70 mA | 2.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL7302MG | 730 nm | 40 mW | 75 mA | 2.5 V | 9° | 18° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L760VH1 | 760 nm | 0.5 mW | 3 mA (Max) | 2.2 V | 12° | 12° | Single Frequency | TO-46 |
| DBR760PN | 761 nm | 9 mW | 125 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L763VH1 | 763 nm | 0.5 mW | 3 mA (Max) | 2.0 V | 10° | 10° | Single Frequency | TO-46 |
| DBR767PN | 767 nm | 23 mW | 220 mA | 1.87 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DBR770PN | 770 nm | 35 mW | 220 mA | 1.92 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L780P010 | 780 nm | 10 mW | 24 mA | 1.8 V | 8° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| DBR780PN | 780 nm | 45 mW | 250 mA | 1.9 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| ULN780PC | 780 nm | 70 mW | 600 mA | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L785P5 | 785 nm | 5 mW | 28 mA | 1.9 V | 10° | 29° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LPS-PM785-FC | 785 nm | 6.5 mW | 60 mA | - | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, PM Pigtail |
| LPS-785-FC | 785 nm | 10 mW | 65 mA | 1.85 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP785-SF20 | 785 nm | 20 mW | 85 mA | 1.9 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| DBR785S | 785 nm | 25 mW | 230 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| DBR785P | 785 nm | 25 mW | 230 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L785P25 | 785 nm | 25 mW | 45 mA | 1.9 V | 8° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| FPV785S | 785 nm | 50 mW | 410 mA | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| FPV785P | 785 nm | 50 mW | 410 mA | 2.1 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| LP785-SAV50 | 785 nm | 50 mW | 500 mA | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L785P090 | 785 nm | 90 mW | 125 mA | 2.0 V | 10° | 17° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP785-SF100 | 785 nm | 100 mW | 300 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| FPL785P | 785 nm | 200 mW | 500 mA | 2.1 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| FPL785S-250 | 785 nm | 250 mW (Min) | 500 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| LD785-SEV300 | 785 nm | 300 mW | 500 mA (Max) | 2.0 V | 8° | 16° | Single Frequency | Ø9 mm |
| LD785-SH300 | 785 nm | 300 mW | 400 mA | 2.0 V | 7° | 18° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| FPL785C | 785 nm | 300 mW | 400 mA | 2.0 V | 7° | 18° | Single Transverse Mode | 3 mm x 5 mm Submount |
| LD785-SE400 | 785 nm | 400 mW | 550 mA | 2.0 V | 7° | 16° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| FPV785M | 785 nm | 600 mW | 1100 mA | 1.9 V | - | - | Multimode | Butterfly, MM Pigtail |
| L795VH1 | 795 nm | 0.25 mW | 1.2 mA | 1.8 V | 20° | 12° | Single Frequency | TO-46 |
| DBR795PN | 795 nm | 40 mW | 230 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| ULN795PC | 795 nm | 100 mW | 700 mA | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DBR808PN | 808 nm | 42 mW | 250 mA | 2 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| LP808-SA60 | 808 nm | 60 mW | 150 mA | 1.9 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| M9-808-0150 | 808 nm | 150 mW | 180 mA | 1.9 V | 8° | 17° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| L808P200 | 808 nm | 200 mW | 260 mA | 2 V | 10° | 30° | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm |
| FPL808P | 808 nm | 200 mW | 600 mA | 2.1 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| FPL808S | 808 nm | 200 mW | 750 mA | 2.3 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| L808H1 | 808 nm | 300 mW | 400 mA | 2.1 V | 14° | 6° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| LD808-SE500 | 808 nm | 500 mW | 750 mA | 2.2 V | 7° | 14° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| LD808-SEV500 | 808 nm | 500 mW | 800 mA (Max) | 2.2 V | 8° | 14° | Single Frequency | Ø9 mm |
| L808P500MM | 808 nm | 500 mW | 650 mA | 1.8 V | 12° | 30° | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L808P1000MM | 808 nm | 1000 mW | 1100 mA | 2 V | 9° | 30° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| DBR816PN | 816 nm | 45 mW | 250 mA | 1.95 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| LP820-SF80 | 820 nm | 80 mW | 230 mA | 2.3 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L820P100 | 820 nm | 100 mW | 145 mA | 2.1 V | 9° | 17° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L820P200 | 820 nm | 200 mW | 250 mA | 2.4 V | 9° | 17° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| DBR828PN | 828 nm | 24 mW | 250 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| LPS-830-FC | 830 nm | 10 mW | 120 mA | - | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LPS-PM830-FC | 830 nm | 10 mW | 50 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, PM Pigtail |
| LP830-SF30 | 830 nm | 30 mW | 115 mA | 1.9 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| HL8338MG | 830 nm | 50 mW | 75 mA | 1.9 V | 9° | 22° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L830H1 | 830 nm | 250 mW | 3 A (Max) | 2 V | 8° | 10° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| FPL830P | 830 nm | 300 mW | 900 mA | 2.22 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| FPL830S | 830 nm | 350 mW | 900 mA | 2.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| LD830-SE650 | 830 nm | 650 mW | 900 mA | 2.3 V | 7° | 13° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| LD830-MA1W | 830 nm | 1 W | 2 A | 2.1 V | 7° | 24° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| LD830-ME2W | 830 nm | 2 W | 3 A (Max) | 2.0 V | 8° | 21° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| L840P200 | 840 nm | 200 mW | 255 mA | 2.4 V | 9 | 17 | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L850VH1 | 850 nm | 1 mW | 6 mA (Max) | 2 V | 12° | 12° | Single Frequency | TO-46 |
| L850P010 | 850 nm | 10 mW | 50 mA | 2 V | 10° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L850P030 | 850 nm | 30 mW | 65 mA | 2 V | 8.5° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| FPV852S | 852 nm | 20 mW | 400 mA | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| FPV852P | 852 nm | 20 mW | 400 mA | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DBR852PN | 852 nm | 24 mW | 300 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| LP852-SF30 | 852 nm | 30 mW | 115 mA | 1.9 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L852P50 | 852 nm | 50 mW | 75 mA | 1.9 V | 9° | 22° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP852-SF60 | 852 nm | 60 mW | 150 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L852P100 | 852 nm | 100 mW | 120 mA | 1.9 V | 8° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| ULN852PC | 852 nm | 100 mW | 700 mA | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L852P150 | 852 nm | 150 mW | 170 mA | 1.9 V | 8° | 18° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| L852SEV1 | 852 nm | 270 mW | 400 mA (Max) | 2.0 V | 9° | 12° | Single Frequency | Ø9 mm |
| L852H1 | 852 nm | 300 mW | 415 mA (Max) | 2 V | 7° | 15° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| FPL852P | 852 nm | 300 mW | 900 mA | 2.35 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| FPL852S | 852 nm | 350 mW | 900 mA | 2.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| LD852-SE600 | 852 nm | 600 mW | 950 mA | 2.3 V | 7° (1/e2) | 13° (1/e2) | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| LD852-SEV600 | 852 nm | 600 mW | 1050 mA (Max) | 2.2 V | 8° | 13° (1/e2) | Single Frequency | Ø9 mm |
| LP880-SF3 | 880 nm | 3 mW | 25 mA | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L880P010 | 880 nm | 10 mW | 30 mA | 2.0 V | 12° | 37° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L895VH1 | 895 nm | 0.2 mW | 1.4 mA | 1.6 V | 20° | 13° | Single Frequency | TO-46 |
| DBR895PN | 895 nm | 12 mW | 300 mA | 2 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| LP904-SF3 | 904 nm | 3 mW | 30 mA | 1.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L904P010 | 904 nm | 10 mW | 50 mA | 2.0 V | 10° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP915-SF40 | 915 nm | 40 mW | 130 mA | 1.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| DBR935PN | 935 nm | 13 mW | 300 mA | 1.75 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| LP940-SF30 | 940 nm | 30 mW | 90 mA | 1.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| M9-940-0200 | 940 nm | 200 mW | 270 mA | 1.9 V | 8° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| L960H1 | 960 nm | 250 mW | 400 mA | 2.1 V | 11° | 12° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| FPV976S | 976 nm | 30 mW | 400 mA (Max) | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| FPV976P | 976 nm | 30 mW | 400 mA (Max) | 2.2 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DBR976PN | 976 nm | 33 mW | 450 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L976SEV1 | 976 nm | 270 mW | 400 mA (Max) | 2.0 V | 9° | 12° | Single Frequency | Ø9 mm |
| BL976-SAG3 | 976 nm | 300 mW | 470 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| BL976-PAG500 | 976 nm | 500 mW | 830 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| BL976-PAG700 | 976 nm | 700 mW | 1090 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| BL976-PAG900 | 976 nm | 900 mW | 1480 mA | 2.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L980P010 | 980 nm | 10 mW | 25 mA | 2 V | 10° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP980-SF15 | 980 nm | 15 mW | 70 mA | 1.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L980P030 | 980 nm | 30 mW | 50 mA | 1.5 V | 10° | 35° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| L980P100A | 980 nm | 100 mW | 150 mA | 1.6 V | 6° | 32° | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP980-SA60 | 980 nm | 60 mW | 230 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| L980H1 | 980 nm | 200 mW | 300 mA (Max) | 2.0 V | 8° | 13° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| L980P200 | 980 nm | 200 mW | 300 mA | 1.5 V | 6° | 30° | Multimode | Ø5.6 mm |
| DBR1060SN | 1060 nm | 130 mW | 650 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| DBR1060PN | 1060 nm | 130 mW | 650 mA | 1.8 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DBR1064S | 1064 nm | 40 mW | 150 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| DBR1064P | 1064 nm | 40 mW | 150 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DBR1064PN | 1064 nm | 110 mW | 550 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| LPS-1060-FC | 1064 nm | 50 mW | 220 mA | 1.4 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm, SM Pigtail |
| M9-A64-0200 | 1064 nm | 200 mW | 280 mA | 1.7 V | 8° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| L1064H1 | 1064 nm | 300 mW | 700 mA | 1.92 V | 7.6° | 13.5° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| L1064H2 | 1064 nm | 450 mW | 1100 mA | 1.92 V | 7.6° | 13.5° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| DBR1083PN | 1083 nm | 100 mW | 500 mA | 1.75 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L1270P5DFB | 1270 nm | 5 mW | 15 mA | 1.1 V | 7° | 9° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP1270-SAD2 | 1270 nm | 15 mW | 100 mA (Max) | 1.3 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP1270-PAD2 | 1270 nm | 15 mW | 100 mA (Max) | 1.3 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, PM Pigtail |
| L1290P5DFB | 1290 nm | 5 mW | 16 mA | 1.0 V | 7° | 9° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP1290-SAD2 | 1290 nm | 15 mW | 100 mA (Max) | 1.3 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP1290-PAD2 | 1290 nm | 15 mW | 100 mA (Max) | 1.3 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, PM Pigtail |
| LP1310-SAD2 | 1310 nm | 2.0 mW | 40 mA | 1.1 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP1310-PAD2 | 1310 nm | 2.0 mW | 40 mA | 1.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, PM Pigtail |
| L1310P5DFB | 1310 nm | 5 mW | 16 mA | 1.0 V | 7° | 9° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| LPSC-1310-FC | 1310 nm | 50 mW | 350 mA | 2 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| FPL1053S | 1310 nm | 130 mW | 400 mA | 1.7 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| FPL1053P | 1310 nm | 130 mW | 400 mA | 1.7 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| FPL1053T | 1310 nm | 300 mW (Pulsed) | 750 mA | 2 V | 15° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| FPL1053C | 1310 nm | 300 mW (Pulsed) | 750 mA | 2 V | 15° | 27° | Single Transverse Mode | Chip on Submount |
| L1310G1 | 1310 nm | 2000 mW | 5 A | 1.5 V | 7° | 24° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| DFB1320P | 1320 nm | 250 mW (Min) | 1800 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L1330P5DFB | 1330 nm | 5 mW | 14 mA | 1.0 V | 7° | 9° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| LP1330-SAD2 | 1330 nm | 15 mW | 100 mA (Max) | 1.3 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP1330-PAD2 | 1330 nm | 15 mW | 100 mA (Max) | 1.3 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, PM Pigtail |
| L1370G1 | 1370 nm | 2000 mW | 5 A | 1.4 V | 6° | 22° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| BL1425-PAG500 | 1425 nm | 500 mW | 1600 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| BL1436-PAG500 | 1436 nm | 500 mW | 1600 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L1450G1 | 1450 nm | 2000 mW | 5 A | 1.4 V | 7° | 22° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| BL1456-PAG500 | 1456 nm | 500 mW | 1600 mA | 2.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L1470P5DFB | 1470 nm | 5 mW | 19 mA | 1.0 V | 7° | 9° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| L1480G1 | 1480 nm | 2000 mW | 5 A | 1.6 V | 6° | 20° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| L1490P5DFB | 1490 nm | 5 mW | 24 mA | 1.0 V | 7° | 9° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| L1510P5DFB | 1510 nm | 5 mW | 20 mA | 1.0 V | 7° | 9° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| L1530P5DFB | 1530 nm | 5 mW | 21 mA | 1.0 V | 7° | 9° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| LPS-1550-FC | 1550 nm | 1.5 mW | 30 mA | 1.0 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LPS-PM1550-FC | 1550 nm | 1.5 mW | 30 mA | 1.1 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP1550-SAD2 | 1550 nm | 2.0 mW | 40 mA | 1.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| LP1550-PAD2 | 1550 nm | 2.0 mW | 40 mA | 1.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm, PM Pigtail |
| L1550P5DFB | 1550 nm | 5 mW | 20 mA | 1.0 V | 8° | 10° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| ML925B45F | 1550 nm | 5 mW | 30 mA | 1.1 V | 25° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| SFL1550S | 1550 nm | 40 mW | 300 mA | 1.5 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| SFL1550P | 1550 nm | 40 mW | 300 mA | 1.5 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| LPSC-1550-FC | 1550 nm | 50 mW | 250 mA | 2 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| FPL1009S | 1550 nm | 100 mW | 400 mA | 1.4 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| FPL1009P | 1550 nm | 100 mW | 400 mA | 1.4 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| ULN15PC | 1550 nm | 140 mW | 650 mA | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Extended Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| ULN15PT | 1550 nm | 140 mW | 650 mA | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Extended Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| FPL1001C | 1550 nm | 150 mW | 400 mA | 1.4 V | 18° | 31° | Single Transverse Mode | Chip on Submount |
| FPL1055T | 1550 nm | 300 mW (Pulsed) | 750 mA | 2 V | 15° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| FPL1055C | 1550 nm | 300 mW (Pulsed) | 750 mA | 2 V | 15° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Chip on Submount |
| L1550G1 | 1550 nm | 1700 mW | 5 A | 1.5 V | 7° | 28° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| DFB1550 | 1555 nm | 100 mW (Min) | 1000 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| DFB1550T | 1555 nm | 130 mW (Min) | 800 mA (Max) | 1.7 V | - | - | Single-Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| DFB1550N | 1555 nm | 130 mW (Min) | 1800 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| DFB1550P | 1555 nm | 100 mW (Min) | 1000 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DFB1550PN | 1555 nm | 130 mW (Min) | 1800 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| L1570P5DFB | 1570 nm | 5 mW | 25 mA | 1.0 V | 7° | 9° | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| L1575G1 | 1575 nm | 1700 mW | 5 A | 1.5 V | 6° | 28° | Multimode | Ø9 mm |
| LPSC-1625-FC | 1625 nm | 50 mW | 350 mA | 1.5 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm, SM Pigtail |
| FPL1054S | 1625 nm | 80 mW | 400 mA | 1.7 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| FPL1054P | 1625 nm | 80 mW | 400 mA | 1.7 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| FPL1054C | 1625 nm | 250 mW (Pulsed) | 750 mA | 2 V | 15° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Chip on Submount |
| FPL1054T | 1625 nm | 200 mW (Pulsed) | 750 mA | 2 V | 15° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| DFB1642T | 1642 nm | 80 mW (Min) | 600 mA (Max) | 1.8 V | - | - | Single-Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| DFB1642 | 1642 nm | 80 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| DFB1642P | 1642 nm | 80 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DFB1646 | 1646 nm | 80 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| DFB1646P | 1646 nm | 80 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DFB1650T | 1649 nm | 80 mW (Min) | 800 mA (Max) | 1.7 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| FPL1059S | 1650 nm | 80 mW | 400 mA | 1.7 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| FPL1059P | 1650 nm | 80 mW | 400 mA | 1.7 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| DFB1650 | 1650 nm | 80 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| DFB1650P | 1650 nm | 80 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| FPL1059C | 1650 nm | 225 mW (Pulsed) | 750 mA | 2 V | 15° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Chip on Submount |
| FPL1059T | 1650 nm | 225 mW (Pulsed) | 750 mA | 2 V | 15° | 28° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø5.6 mm |
| DFB1654T | 1653 nm | 80 mW (Min) | 800 mA (Max) | 1.4 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Ø5.6 mm |
| DFB1654 | 1654 nm | 80 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| DFB1654P | 1654 nm | 80 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 3.0 V | - | - | Single Frequency | Butterfly, PM Pigtail |
| FPL1940S | 1940 nm | 15 mW | 400 mA | 2 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| FPL2000S | 2 µm | 15 mW | 400 mA | 2 V | - | - | Single Transverse Mode | Butterfly, SM Pigtail |
| FPL2000C | 2 µm | 30 mW | 400 mA | 5.2 V | 8° | 19° | Single Transverse Mode | Chip on Submount |
| ID3250HHLH | 3.00 - 3.50 µm (DFB) | 5 mW | 400 mA (Max) | 5 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| IF3400T1 | 3.40 µm (FP) | 30 mW | 300 mA | 4 V | 40° | 70° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| ID3750HHLH | 3.50 - 4.00 µm (DFB) | 5 mW | 300 mA (Max) | 5 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| ID3271HH | 3.271 µm (DFB) | 5 mW | 350 mA (Max) | 5 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| ID3345HH | 3.345 µm (DFB) | 5 mW | 350 mA (Max) | 5 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| ID3596HH | 3.596 µm (DFB) | 5 mW | 300 mA (Max) | 5 V | 5 mrad (0.29°) | 5 mrad (0.29°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QF3850T1 | 3.85 µm (FP) | 200 mW | 600 mA (Max) | 13.5 V | 30° | 40° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| QF3850HHLH | 3.85 µm (FP) | 320 mW (Min) | 1100 mA (Max) | 13 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Transverse Mode | Horizontal HHL |
| QF4040HHLH | 4.05 µm (FP) | 320 mW (Min) | 1100 mA (Max) | 13 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Transverse Mode | Horizontal HHL |
| QD4500CM1 | 4.00 - 5.00 µm (DFB) | 40 mW | 500 mA (Max) | 10.5 V | 30° | 40° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD4500HHLH | 4.00 - 5.00 µm (DFB) | 80 mW | 500 mA (Max) | 11 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QF4050T2 | 4.05 µm (FP) | 70 mW | 250 mA | 12 V | 30° | 40° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| QF4050C2 | 4.05 µm (FP) | 300 mW | 400 mA | 12 V | 30 | 42 | Single Transverse Mode | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QF4050T1 | 4.05 µm (FP) | 300 mW | 600 mA (Max) | 12.0 V | 30° | 40° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| QF4050D2 | 4.05 µm (FP) | 800 mW | 750 mA | 13 V | 30° | 40° | Single Transverse Mode | D-Mount |
| QF4050D3 | 4.05 µm (FP) | 1200 mW | 1000 mA | 13 V | 30° | 40° | Single Transverse Mode | D-Mount |
| QD4235HH | 4.235 µm (DFB) | 80 mW | 500 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD4327HH | 4.327 µm (DFB) | 90 mW | 500 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD4472HH | 4.472 µm (DFB) | 85 mW | 500 mA (Max) | 11 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD4540HH | 4.540 µm (DFB) | 70 mW | 500 mA (Max) | 11 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QF4600T2 | 4.60 µm (FP) | 200 mW | 500 mA (Max) | 13.0 V | 30° | 40° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| QF4600T1 | 4.60 µm (FP) | 400 mW | 800 mA (Max) | 12.0 V | 30° | 40° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| QF4600C2 | 4.60 µm (FP) | 600 mW | 600 mA | 12 V | 30° | 42° | Single Transverse Mode | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QF4600T3 | 4.60 µm (FP) | 1000 mW | 800 mA (Max) | 13 V | 30° | 40° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| QF4600D4 | 4.60 µm (FP) | 2500 mW | 1800 mA | 12.5 V | 40° | 30° | Single Transverse Mode | D-Mount |
| QF4600D3 | 4.60 µm (FP) | 3000 mW | 1700 mA | 12.5 V | 30° | 40° | Single Transverse Mode | D-Mount |
| QD4602HH | 4.602 µm (DFB) | 150 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QF4650HHLH | 4.65 µm (FP) | 1500 mW (Min) | 1100 mA | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Transverse Mode | Horizontal HHL |
| QD5500CM1 | 5.00 - 6.00 µm (DFB) | 40 mW | 700 mA (Max) | 9.5 V | 30° | 45° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD5500HHLH | 5.00 - 6.00 µm (DFB) | 150 mW | 500 mA (Max) | 11 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD5250C2 | 5.20 - 5.30 µm (DFB) | 60 mW | 700 mA (Max) | 9.5 V | 30° | 45° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD5263HH | 5.263 µm (DFB) | 130 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD6500CM1 | 6.00 - 7.00 µm (DFB) | 40 mW | 650 mA (Max) | 10 V | 35° | 50° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD6500HHLH | 6.00 - 7.00 µm (DFB) | 80 mW | 600 mA (Max) | 11 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QF6000HHLH | 6.0 µm (FP) | 200 mW (Min) | 1100 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Transverse Mode | Horizontal HHL |
| QD6134HH | 6.134 µm (DFB) | 50 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD7500CM1 | 7.00 - 8.00 µm (DFB) | 40 mW | 600 mA (Max) | 10 V | 40° | 50° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD7500HHLH | 7.00 - 8.00 µm (DFB) | 50 mW | 700 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD7500DM1 | 7.00 - 8.00 µm (DFB) | 100 mW | 600 mA (Max) | 11.5 V | 40° | 55° | Single Frequency | D-Mount |
| QD7416HH | 7.416 µm (DFB) | 100 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD7716HH | 7.716 µm (DFB) | 30 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QF7900HB | 7.9 µm (FP) | 700 mW | 1600 mA (Max) | 9 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Transverse Mode | Horizontal HHL |
| QD7901HH | 7.901 µm (DFB) | 50 mW | 700 mA (Max) | 10 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD8050CM1 | 8.00 - 8.10 µm (DFB) | 70 mW | 800 mA (Max) | 9 V | 55° | 70° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD8500CM1 | 8.00 - 9.00 µm (DFB) | 100 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 9.5 V | 40° | 55° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD8500HHLH | 8.00 - 9.00 µm (DFB) | 100 mW | 600 mA (Max) | 10.2 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD8496HH | 8.496 µm (DFB) | 100 mW | 800 mA (Max) | 10 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QF8450C2 | 8.45 µm (FP) | 300 mW | 750 mA | 9 V | 40° | 60° | Single Transverse Mode | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QF8500HB | 8.5 µm (FP) | 500 mW | 2000 mA (Max) | 9 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Transverse Mode | Horizontal HHL |
| QD8650CM1 | 8.60 - 8.70 µm (DFB) | 50 mW | 900 mA (Max) | 9.5 V | 55° | 70° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD8912HH | 8.912 µm (DFB) | 150 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD9500CM1 | 9.00 - 10.00 µm (DFB) | 60 mW | 800 mA (Max) | 9.5 V | 40° | 55° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD9500HHLH | 9.00 - 10.00 µm (DFB) | 100 mW | 600 mA (Max) | 10.2 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Transverse Mode | Horizontal HHL |
| QD9062HH | 9.062 µm (DFB) | 130 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QF9150C2 | 9.15 µm (FP) | 200 mW | 850 mA | 11 V | 40° | 60° | Single Transverse Mode | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QF9200HB | 9.2 µm (FP) | 250 mW | 2000 mA (Max) | 9 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Transverse Mode | Horizontal HHL |
| QF9500T1 | 9.5 µm (FP) | 300 mW | 550 mA | 12 V | 40° | 55° | Single Transverse Mode | Ø9 mm |
| QF9500HHLH | 9.5 µm (FP) | 400 mW (Min) | 1200 mA (Max) | 11 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD9550C2 | 9.50 - 9.60 µm (DFB) | 60 mW | 800 mA (Max) | 9.5 V | 40° | 55° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD9697HH | 9.697 µm (DFB) | 80 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD10500CM1 | 10.00 - 11.00 µm (DFB) | 40 mW | 600 mA (Max) | 10 V | 40° | 55° | Single Frequency | Two-Tab C-Mount |
| QD10500HHLH | 10.00 - 11.00 µm (DFB) | 50 mW | 700 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD10530HH | 10.530 µm (DFB) | 50 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QD10549HH | 10.549 µm (DFB) | 60 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| QF10600HHLH | 10.6 µm (FP) | 200 mW (Min) | 1500 mA (Max) | 10 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Transverse Mode | Horizontal HHL |
| QD10622HH | 10.622 µm (DFB) | 60 mW | 1000 mA (Max) | 12 V | 6 mrad (0.34°) | 6 mrad (0.34°) | Single Frequency | Horizontal HHL |
| The rows shaded green above denote single-frequency lasers. |











 Products Home
Products Home




















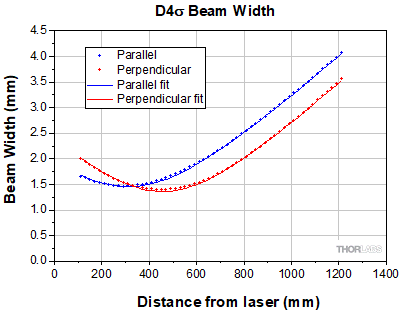

 MIR Quantum and Interband Cascade Lasers
MIR Quantum and Interband Cascade Lasers